Error 404 not found is one of the most common HTTP response messages on the web. It means the file or folder you requested is not available on the server (or may be deleted from the server). If the web page is deleted, still you can access the information or content of the page easily.
There are more than 130 trillion individual web pages are exist in Google search. Google creates a cache of each page as a snapshot, so anyone can easily access the webpage even it goes down or not available. Don’t forget about The Wayback Machine who has more than 445 billion web pages cached, and it constantly growing.
Access Deleted Webpages using The Wayback Machine
It lets you view the past of the web. Follow the steps below:
- Go to archive.org/web.
- Type or paste the URL of a deleted webpage.
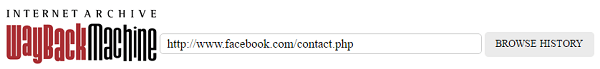
- Click the ‘Browse History’ button.
- Wait while it searching your contentm and also tell you how many times the page was captured.
- Click on a date (highlighted with blue color) and view the web page.
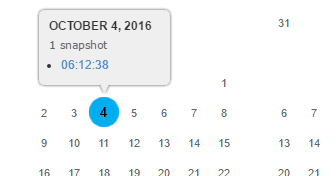
You may close The Wayback Machine toolbar, in order to view the content in full page. The captured page you are watching in the browser is absolutely static. Forms, Media Elements and other such dynamic contents will probably not work.
If a page/link/URL in Google search shows error 404 not found message, you can easily access the cached version of that URL directly from Google search. In a Google search results, click the green down arrow icon, and click ‘Cached’. This will now show you the snapshot of the webpage, with date and time.
The Wayback Machine and Google’s cache server not just useful for accessing deleted pages, even if a site is down, forbidden or blocked, you can still see the information through cached data.
Here are few examples from Internet Archive:
//www.facebook.com/contact.php in 2006.
//froogle.google.com/ in 2006.
[custom-twitter-feeds feed=2]